Research
Read MoreResearch Interests
- Computational Fluid Dynamics : Hydrodynamics, Magneto-hydrodynamics & Radiative transfer
- Particle Acceleration in AGN jets : Modeling Non-Thermal spectral signature
- Space Weather and Space Plasma Modelling
- Accretion disk physics, Jets and Outflow formation.
- Astrophysical Code Development : MPI Parallel Programming, Visualization software tools, best practices of coding with C and Python.
- Inter-Stellar Medium : Shock-Cloud Interaction, Collapse of molecular cores, Shock induced chemistry.
List of Recent Selected Published Works
For latest simulation movies and talks presented by members from our group on on-going work,
please refer to our Youtube Channel
Effects of a Velocity Shear on Double Current Sheet Systems: Explosive Reconnection and Particle Acceleration
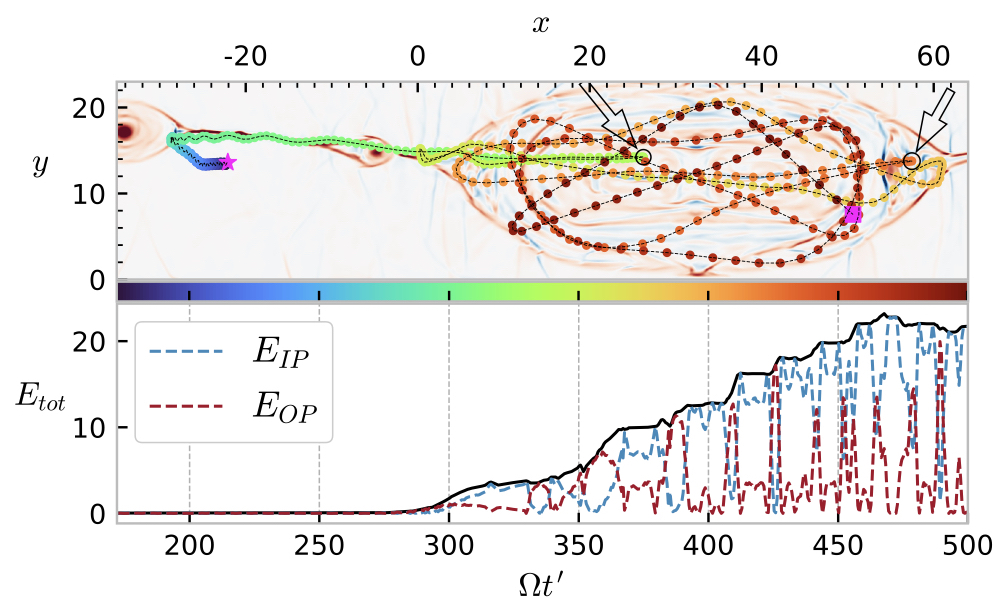
(Top) Trajectory of highest energy particle that is being accelerated due to first order Fermi process within the plasmoid formed due to reconnection (Bottom) Temporal evolution of in plane (IP) and out of plane (OP) components of energy for the particle.
Numerical analysis of long-term variability of AGN jets through RMHD simulations
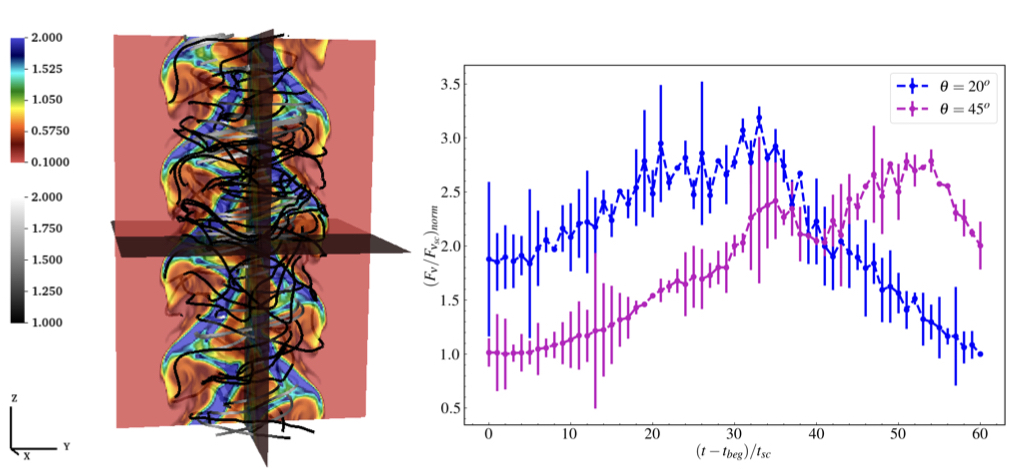
(Left) Density distribution from 3D Relativistic MHD simulations showing kink instability along with tangled magnetic field lines. (Right) Synthetic light curve (for ~ 20 years) generated from kink unstable jet and viewed from two different viewing angles showing long term variablity due to helical jet model.
Jets, disc-winds and oscillations in general relativistic, magnetically driven flows around black hole
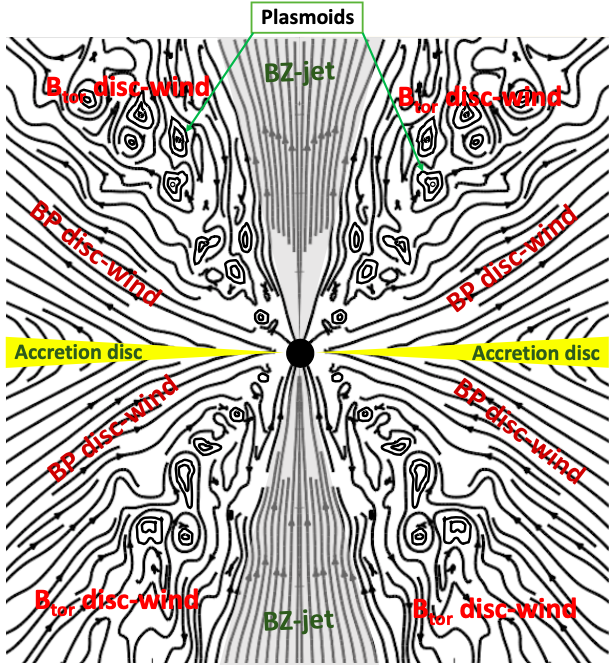
Cartoon figure showing the different jet and wind regions
from our simulations of MAD disc.
Numerical study of Kelvin-Helmholtz instability and its impact on synthetic emission from magnetized jets
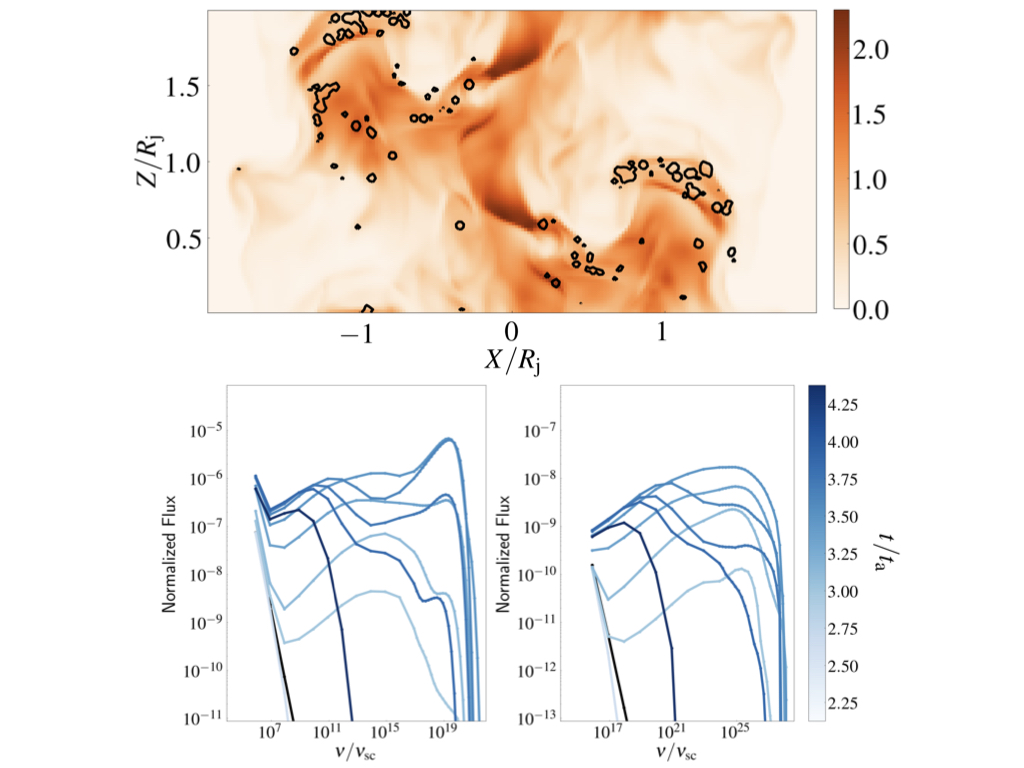
(Top) Production of secondary electron population due to shocks seen in background color image pf density.
(Bottom) The evolution of synthetic SEDs showing synchrotron (left) and IC (right).
Simulating the dynamics and synchrotron emission from relativistic jets II. Evolution of non-thermal electrons
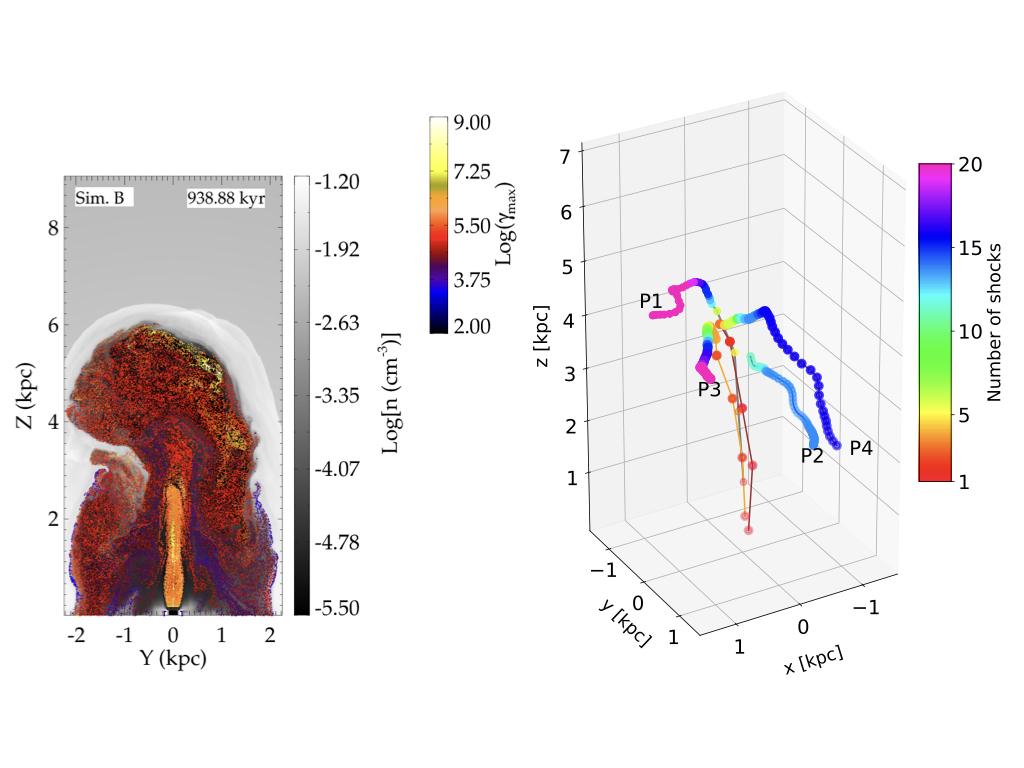
Distribution of particles coloured with their lorentz factor in a jet cocoon.
A comparison study of extrapolation models and empirical relations in forecasting solar wind
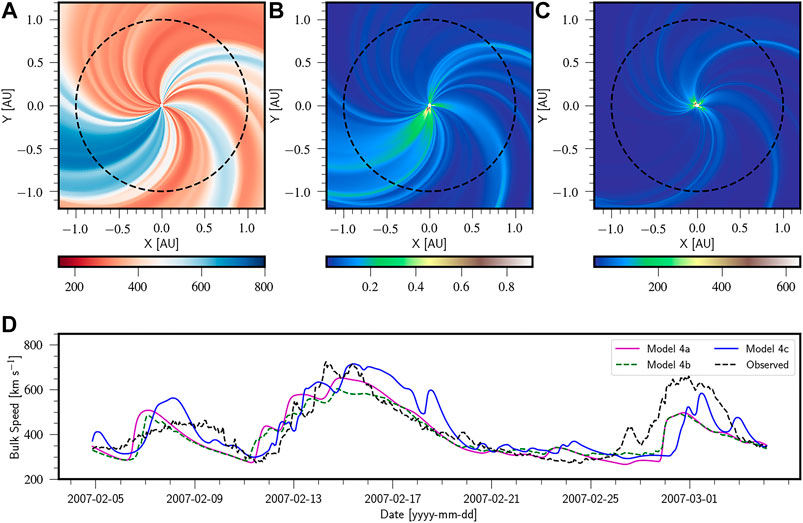
Results obtained from physics based solar wind model
and its comparison with observed data.
A Particle Module for the PLUTO Code. III. Dust
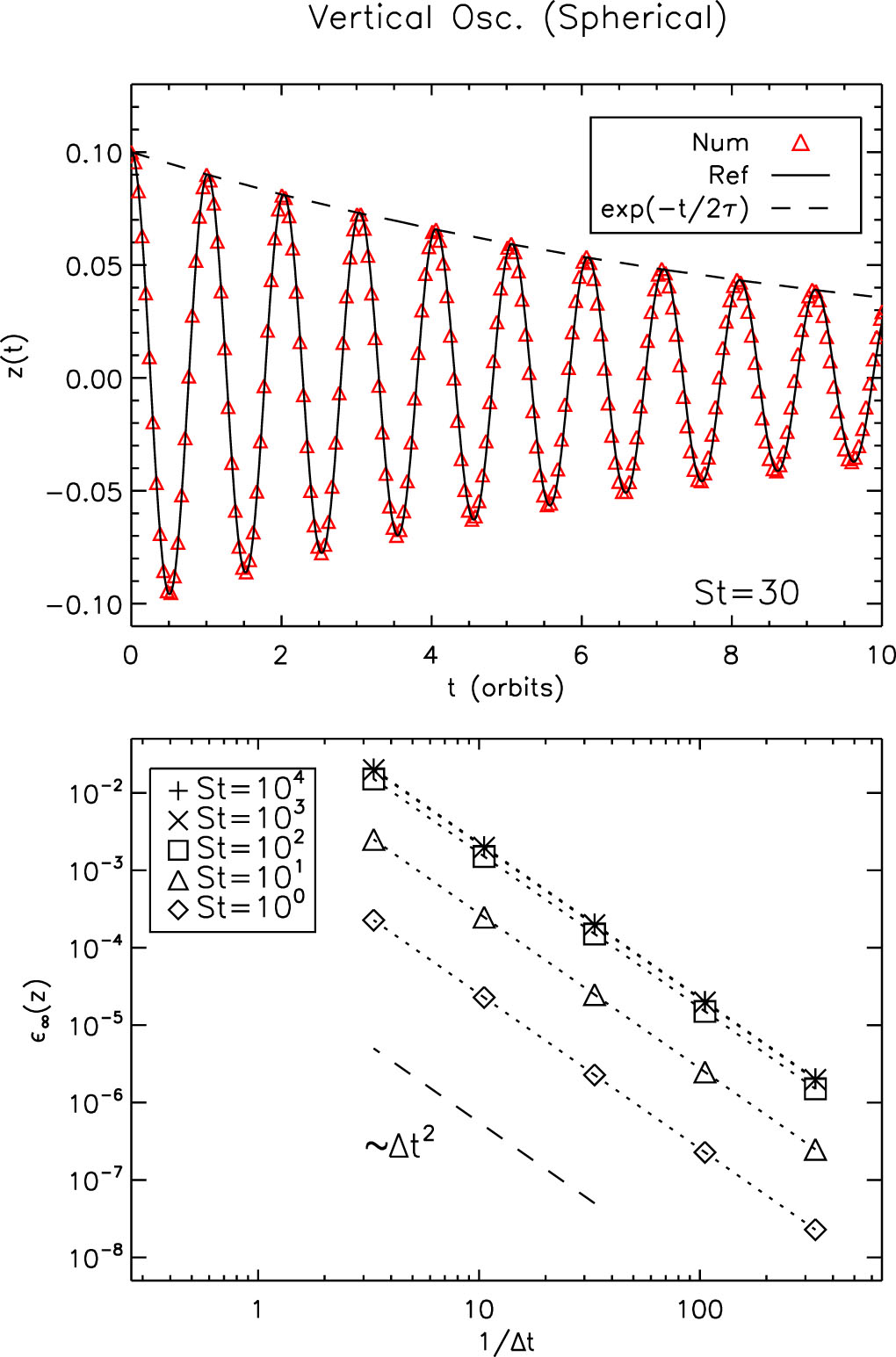
Result for Vertical oscillation test of dust particles
along with convergence study with different Stokes numbers
Modeling Star-Planet Interactions in Far-out Planetary and Exoplanetary Systems
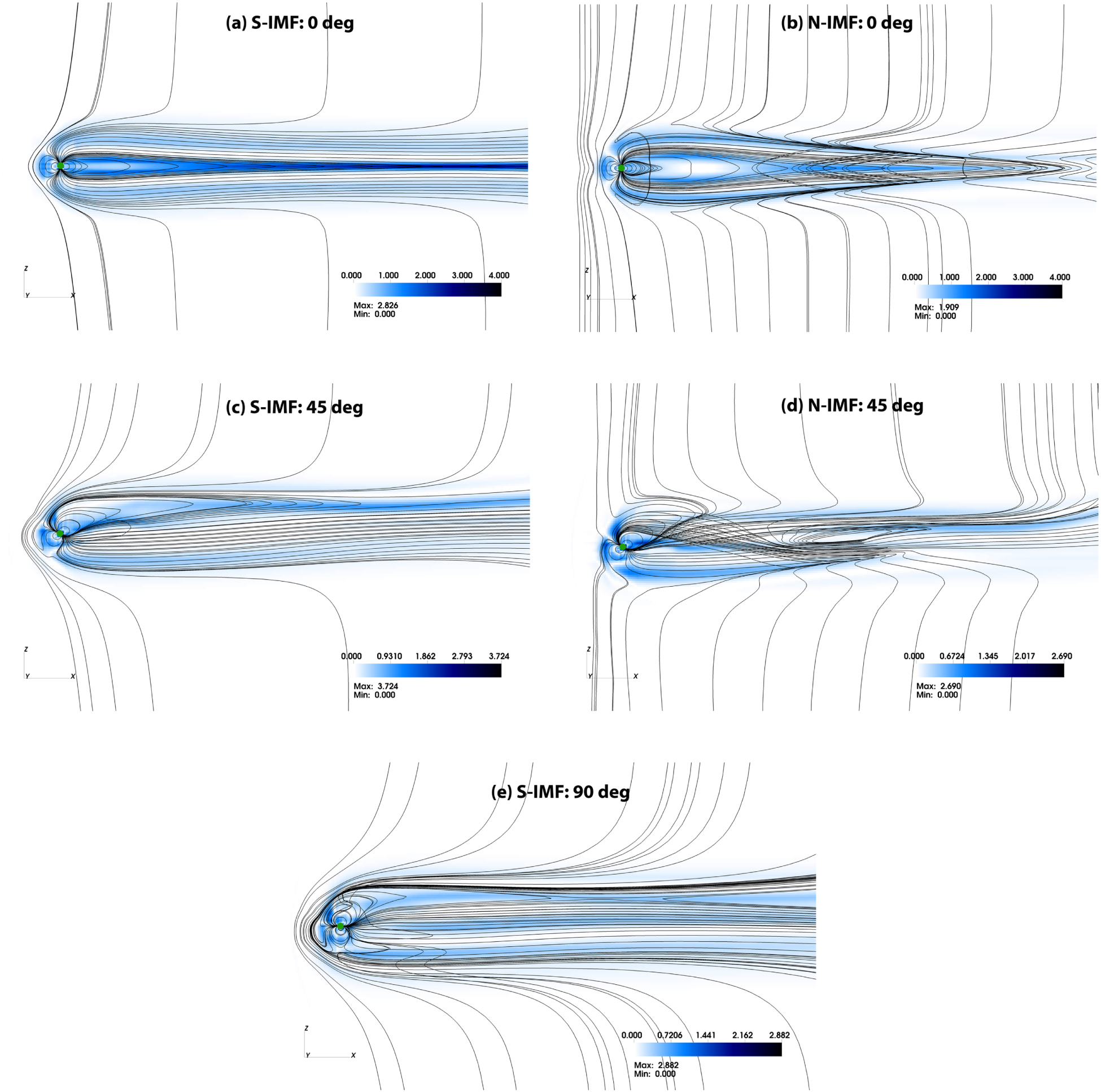
3D steady-state magnetospheric configurations
with no tilt and extreme tilt angles for both S-IMF and N-IMF cases.
A Particle Module for the PLUTO Code II - Hybrid Framework for Modeling Non-thermal emission from Relativistic Magnetized flows
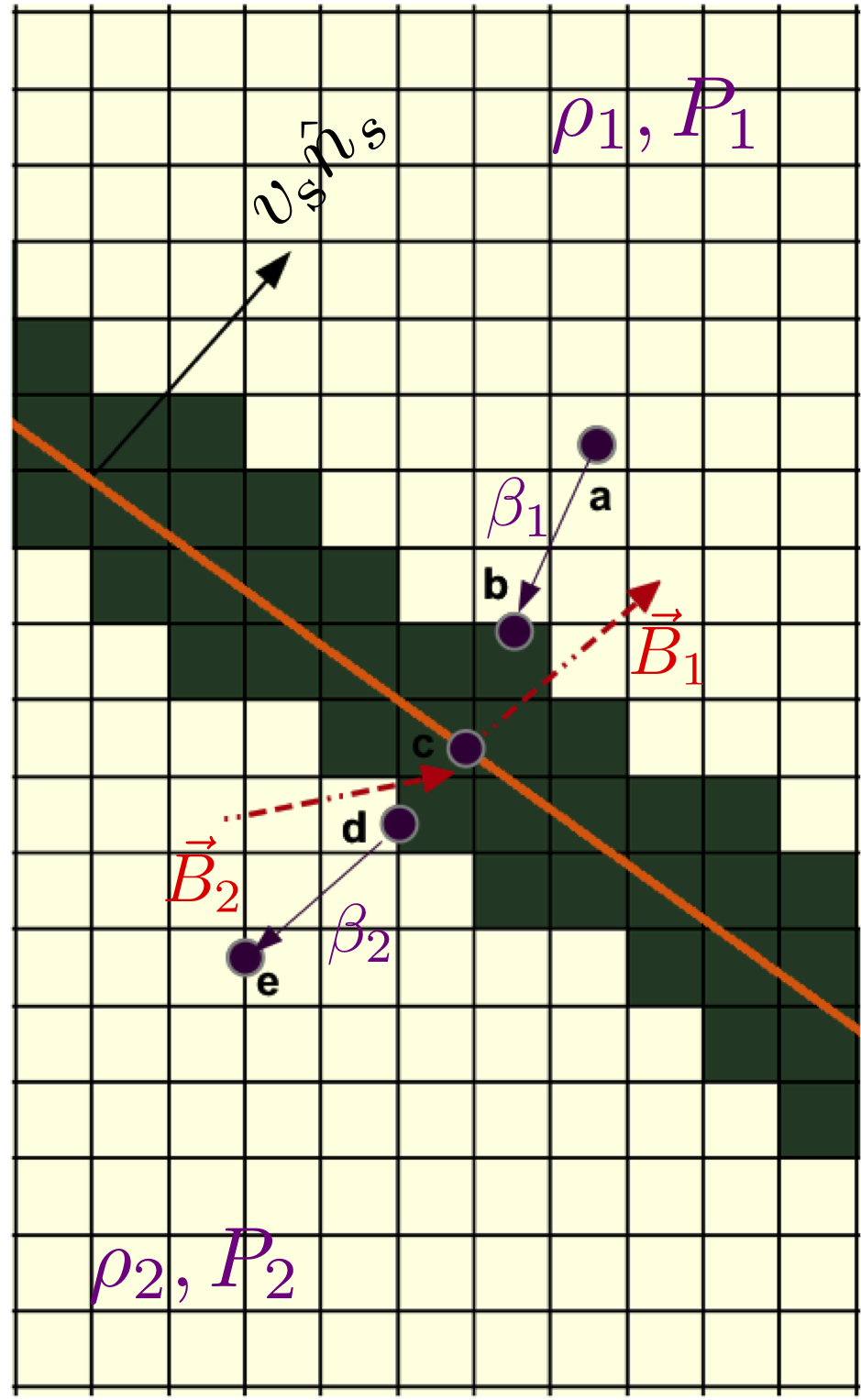
Cartoon figure showing the hybrid framework of
incorporating Lagrangian particles on fixed Eulerian grid.
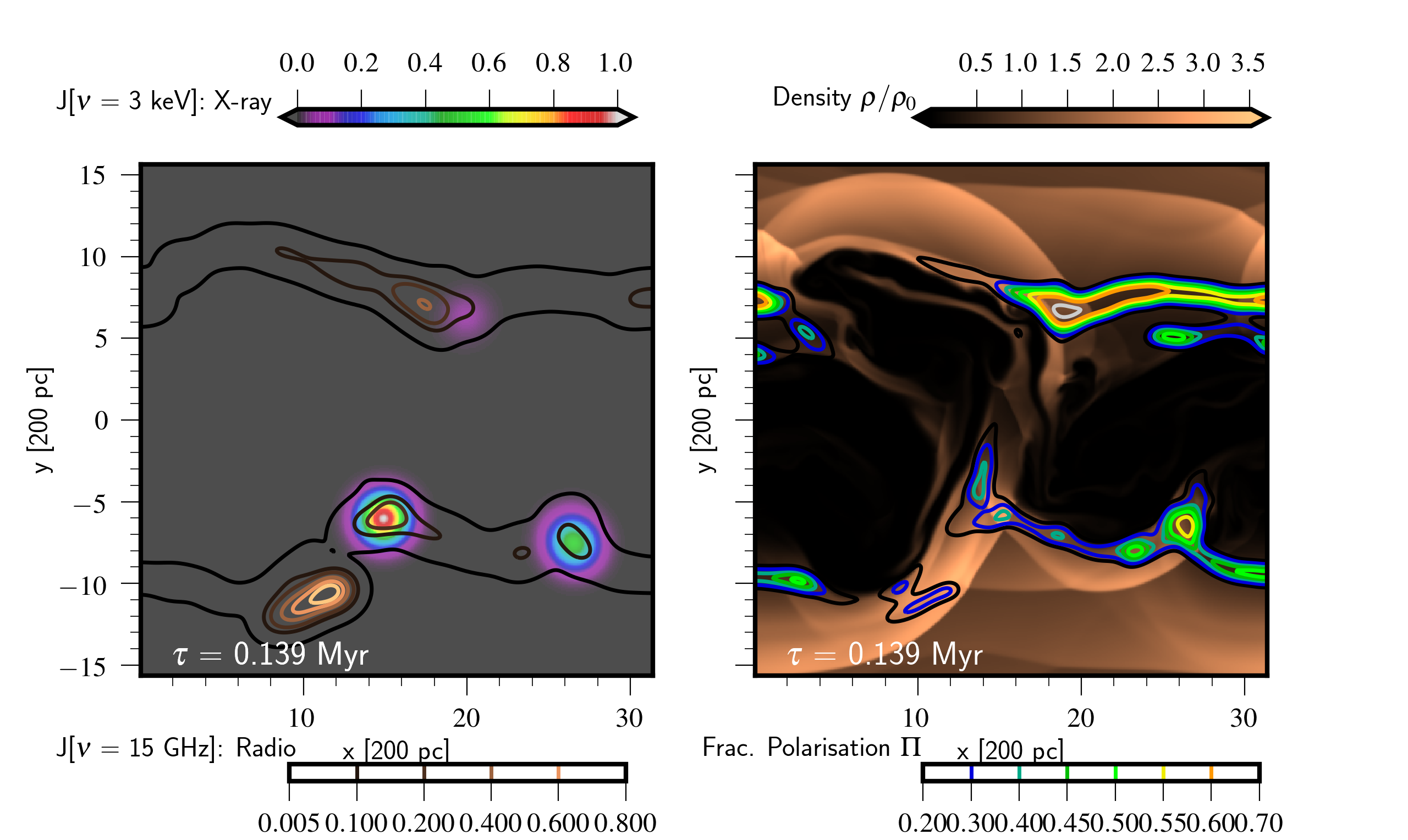
Multi-wavelength emission and polarisation maps of oblique shocks in slab jets.
A Particle Module for the PLUTO Code. I. An Implementation of the MHD–PIC Equations
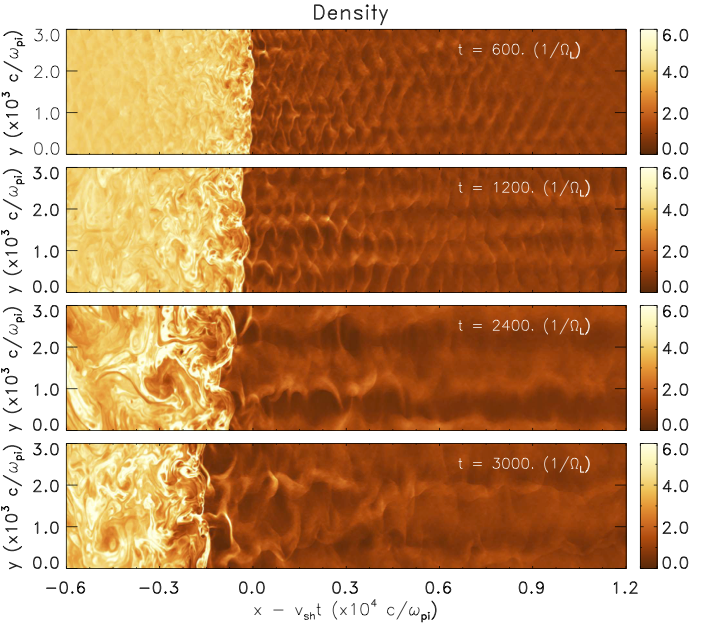
Density snapshots for the collisionless shock problem at four different times. Only a reduced portion of the domain, in proximity of the unperturbed shock position is shown.
Simulation of MHD modes in Active Region of Sun.
There is considerable observational evidence of implosion of magnetic loop systems inside solar coronal active regions following high-energy events like solar flares. In this work, we propose that such collapse can be modeled in three dimensions quite accurately within the framework of ideal magnetohydrodynamics. We furthermore argue that the dynamics of loop implosion is only sensitive to the transmitted disturbance of one or more of the system variables, e.g., velocity generated at the event site. This indicates that to understand loop implosion, it is sensible to leave the event site out of the simulated active region. Toward our goal, a velocity pulse is introduced to model the transmitted disturbance generated at the event site. Magnetic field lines inside our simulated active region are traced in real time, and it is demonstrated that the subsequent dynamics of the simulated loops closely resemble observed imploding loops. Our work highlights the role of plasma β in regards to the rigidity of the loop systems and how that might affect the imploding loops’ dynamics. Compressible magnetohydrodynamic modes such as kink and sausage are also shown to be generated during such processes, in accordance with observations.
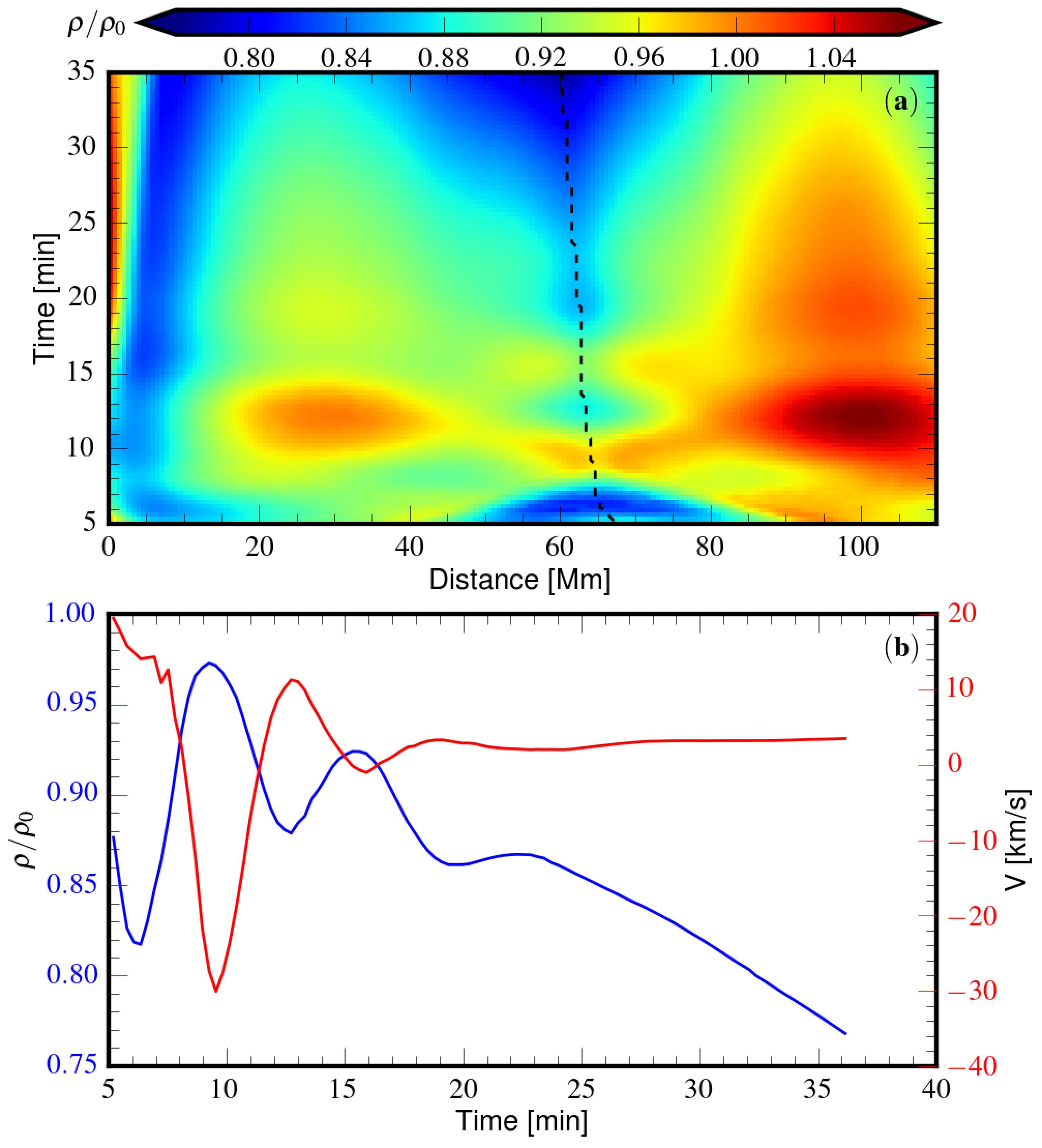
Density evolution along a field line showing indicatication of the standing sausage wave oscillation.
Runge-Kutta Legendre Method for Parabolic PDEs in PLUTO code : Application to Thermal Conduction Problems.
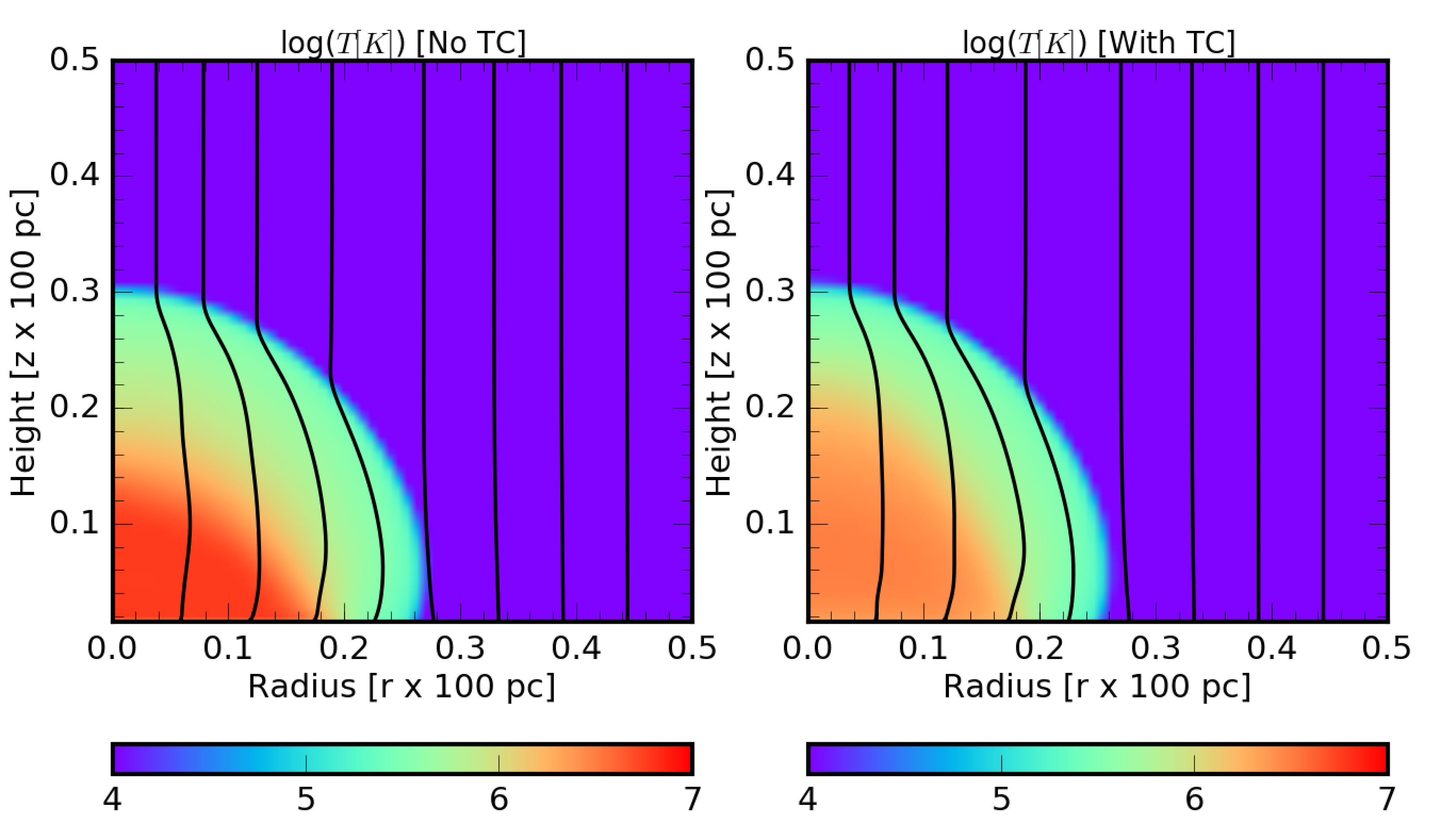
Effect of Anisotropic Thermal conduction in the problem of 2D blast wave.
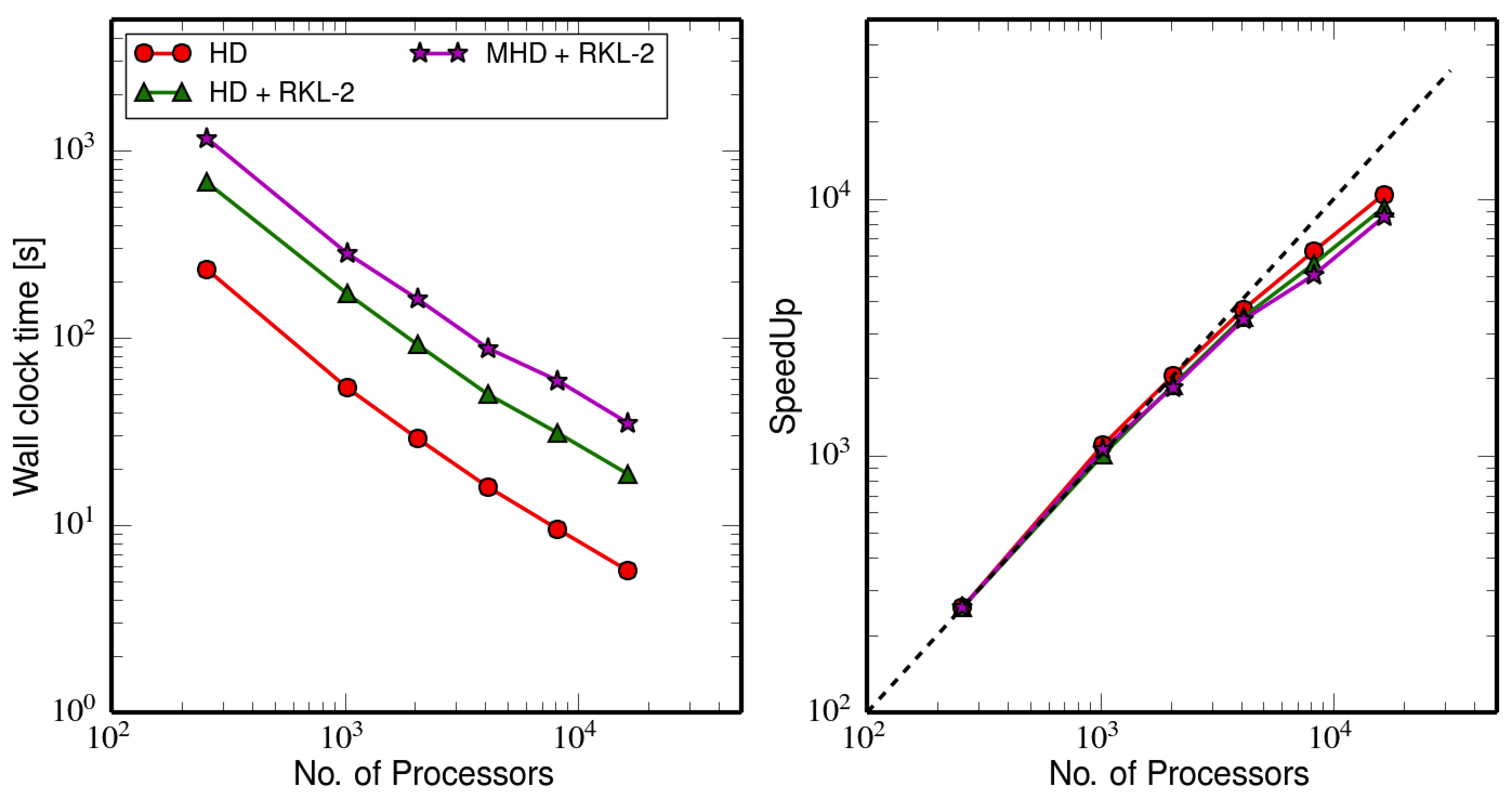
Strong scaling test for the newly implemented Runge-Kutta Legendre Method in PLUTO code.
Interaction of Hydrodynamic Shock with Self-gravitating cloud.
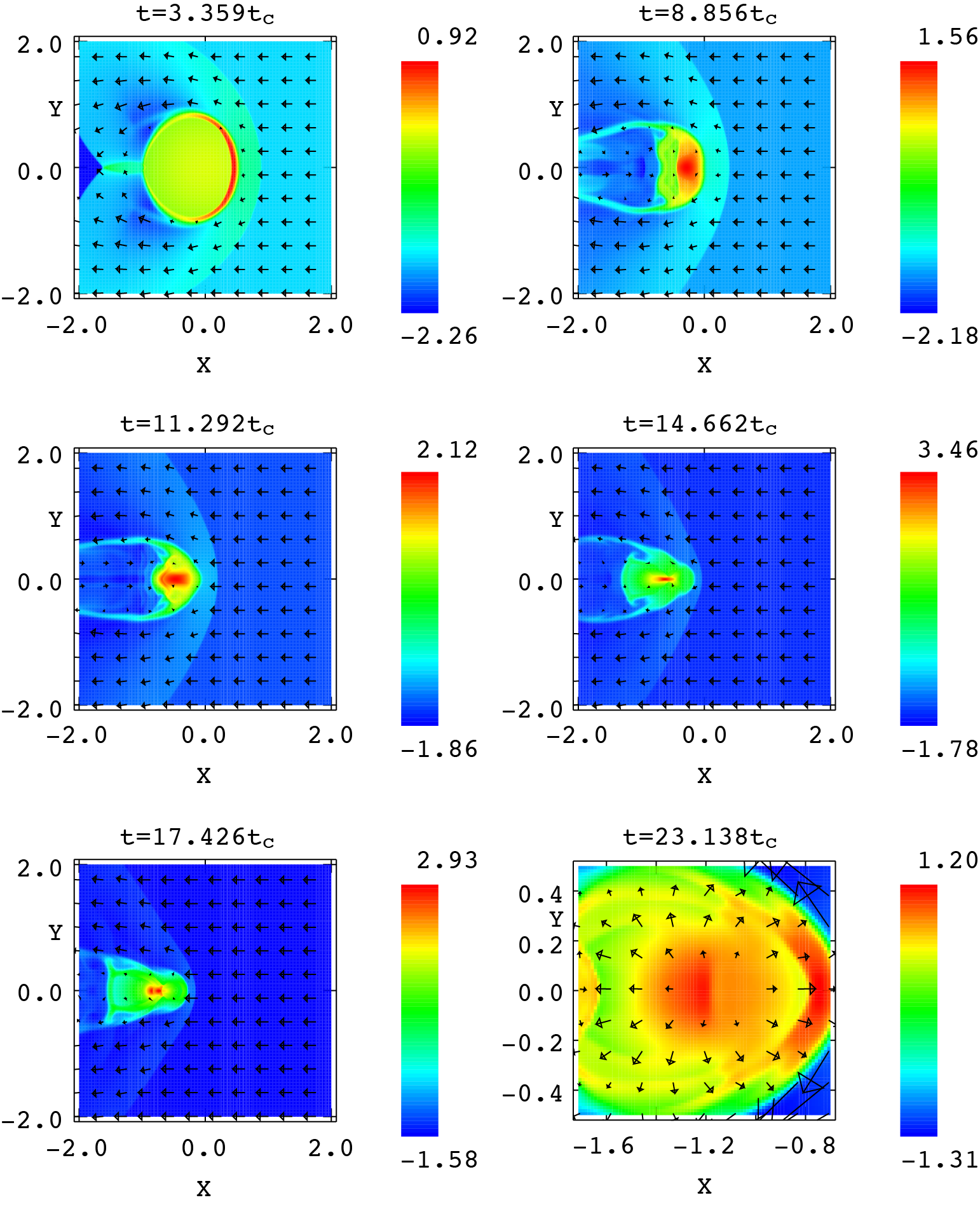
Time evolution of density (X-Y plane) of interaction of 3D self-gravitating cloud with weak shock
Interplay Magnetic reconnection and non-axisymmetric instabilities in Jets.
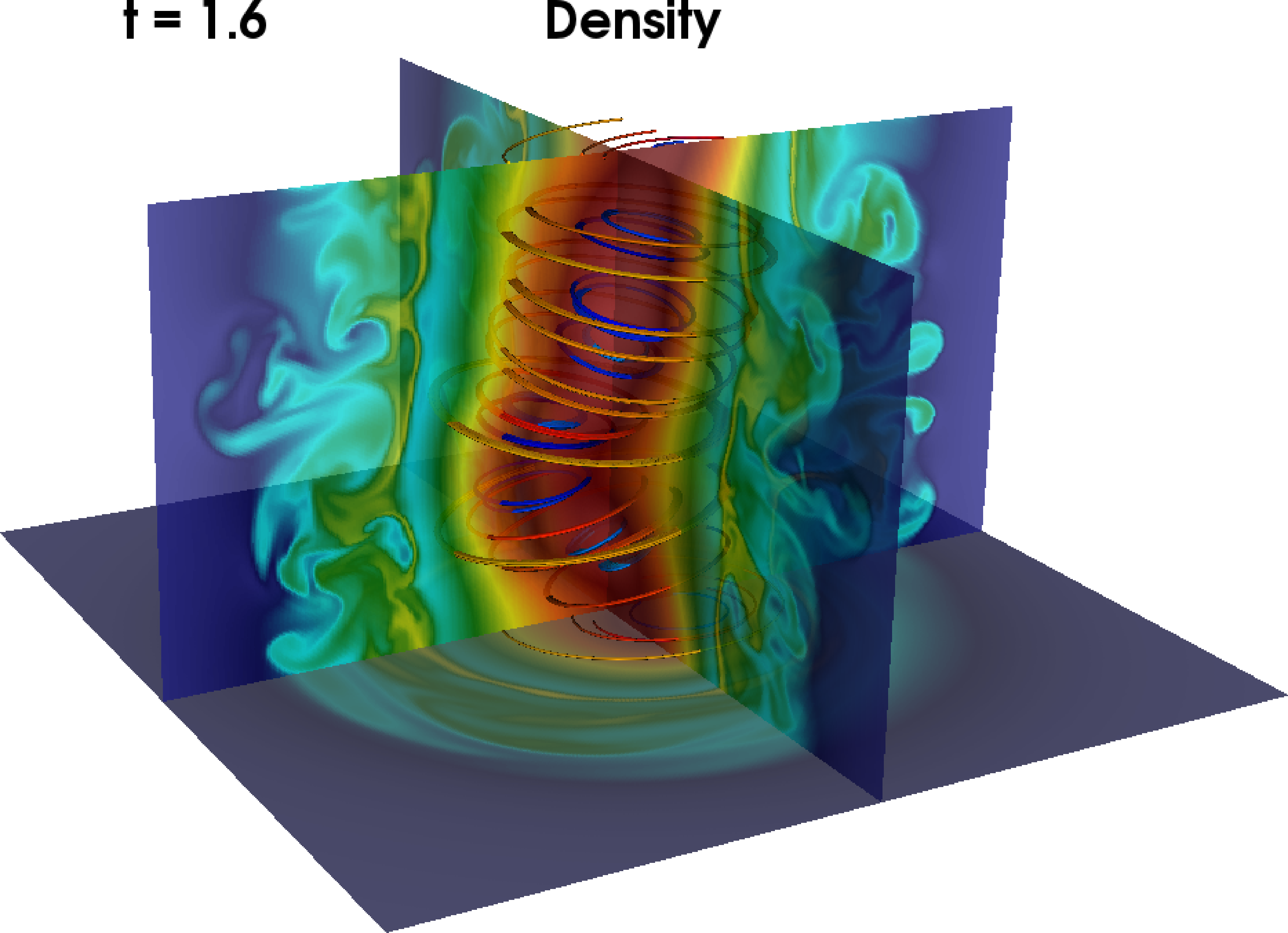
Formation of short wavelength pressure driven instabilities in density of jet column with toroidal magnetic field lines.
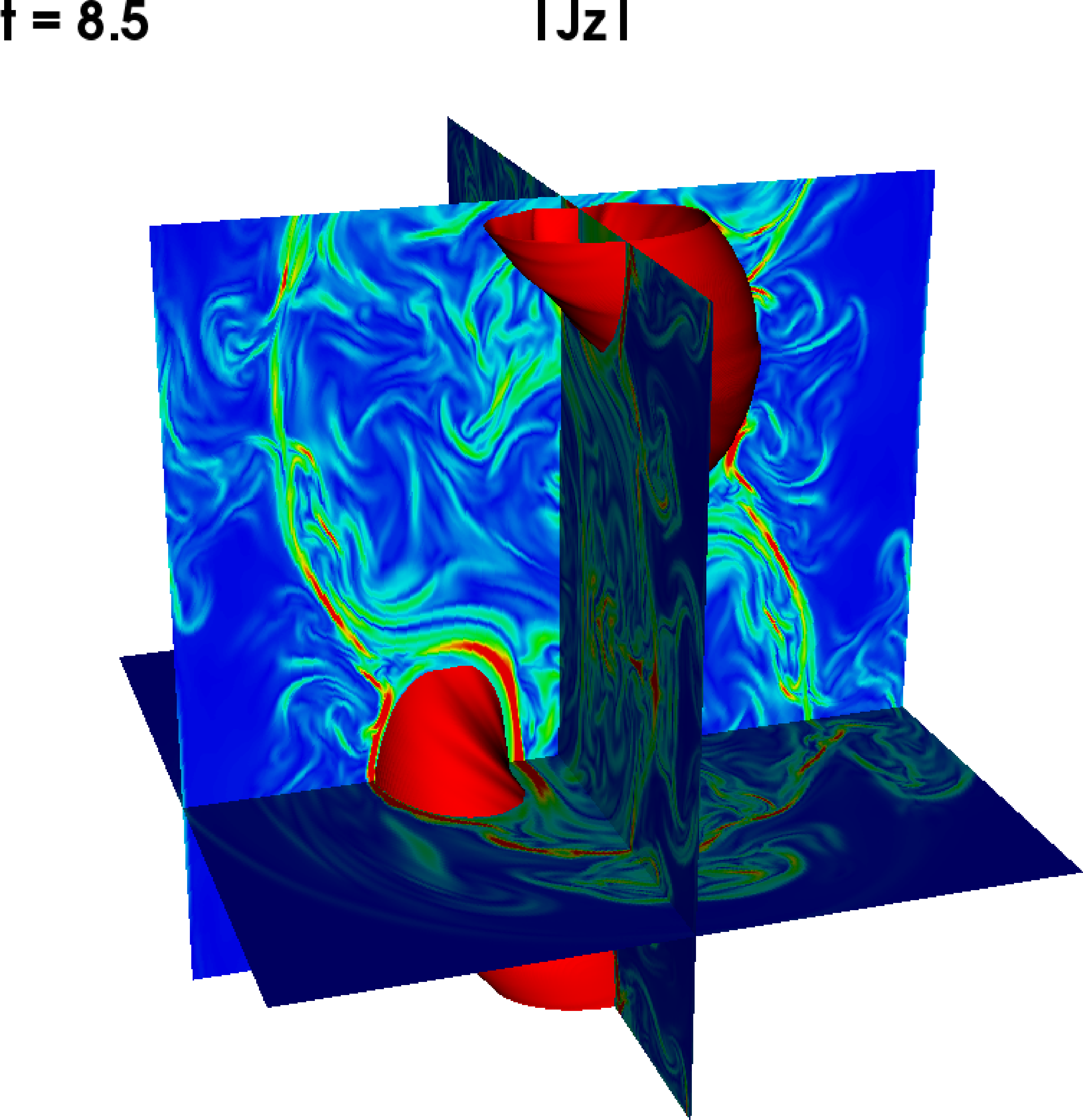
The dominant kink mode for current driven instability seen in the density along turbulent current sheets.